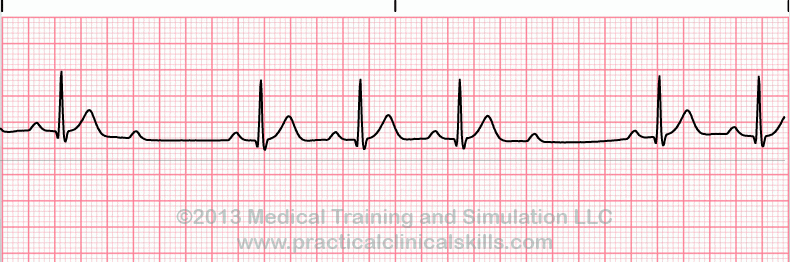
Second Degree Heart Block Type II EKG Interpretation with Rhythm Strip
EKG Features
Rate: Characterized by Atrial rate usually faster than ventricular rate (usually slow)Rhythm: Regular (atrial) and irregular (ventricular)
P Wave: Normal form, but more P waves than QRS complexes
PR Interval: Normal or prolonged
QRS: Normal or wide
A constant P-R interval with missing QRS complexes. Occurring in a specific pattern in a ratio with the P waves.
Second degree Heart Block Mobitz II is characterized by intermittently non-conducted P waves which are not preceded by PR prolongation and are not followed by PR shortening. Mobitz II is usually caused by conduction failure/delay of the His-Purkinje system. In three out of four cases, this conduction block is located distal to the Bundle of His, creating wide QRS complexes. In the other 25% of cases, the block is located within the Bundle of His, producing narrower QRS complexes.
Texas Heart Institute
Second Degree Heart Block Type II EKG Interpretation Example
Return to EKG Reference Guide Index