Third Degree Heart Block - Heart Blocks
Description Part 1
- Third Degree Heart Block is also known as “Complete Heart Block”.
- This name more accurately describes the electrical event or problem occurring within the heart.
- As a result of disease or tissue death, there is a blockage preventing electrical impulses within the atria from entering the ventricular conduction system.
- The outcome of 3rd degree heart block EKG are two independently functioning pacemakers within the heart (typically one is supraventricular, the other is ventricular).
- Essentially, the atria and ventricles are electrically separated (dissociated) from one another.
Description Part 2
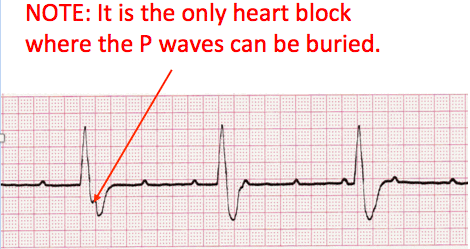
- What will be seen are regularly occurring P waves and QRS complexes, but at two distinctly different rates.
- The QRS complexes may occur as a result of impulses coming from the His bundle or the Purkinje network.
- Morphology and rate will often provide clues regarding the locus of ventricular impulse stimulation. A more narrow appearing QRS with a rate greater than 40 generally would indicate the impulse formation is coming from the His bundle. A wide, bizarre QRS with a rate of 40 or less indicates the impulses are originating in the Purkinje network.
- Complete heart block presents with Regular P to P and R to R intervals and a variable P-R interval.
ECG Practice Strip
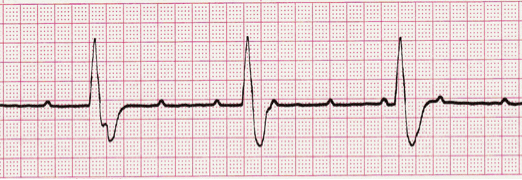
Analyze this tracing using the five steps of rhythm analysis.
Show Answer
- Rhythm: Atria and Ventricles - Regular
- Rate: Atria – 94, Ventricles - 34
- P Wave: Upright (some buried)
- PR interval: Variable
- QRS: 0.14 sec
- Interpretation: Third Degree (Complete) Heart Block
Authors and Sources
Authors and Reviewers
- EKG heart rhythm modules: Thomas O'Brien.
- EKG monitor simulation developer: Steve Collmann
-
12 Lead Course: Dr. Michael Mazzini, MD.
- Spanish language EKG: Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH
- Medical review: Dr. Jonathan Keroes, MD
- Medical review: Dr. Pedro Azevedo, MD, Cardiology
- Last Update: 11/8/2021
Sources
-
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals, 5th Edition
Kathryn Booth and Thomas O'Brien
ISBN10: 1260064778, ISBN13: 9781260064773
McGraw Hill, 2019 -
Rapid Interpretation of EKG's, Sixth Edition
Dale Dublin
Cover Publishing Company -
12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac Drugs
Aaron Reed
Create Space Independent Publishing -
Heart Sounds and Murmurs: A Practical Guide with Audio CD-ROM 3rd Edition
Elsevier-Health Sciences Division
Barbara A. Erickson, PhD, RN, CCRN -
The Virtual Cardiac Patient: A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds, Murmurs, EKG
Jonathan Keroes, David Lieberman
Publisher: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin)
ISBN-10: 0781784425; ISBN-13: 978-0781784429 - Project Semilla, UCLA Emergency Medicine, EKG Training Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH