Sinus Arrest - Sinus Rhythms
Description
- Sinus Arrest occurs when there is a sudden absence of electrical activity initiated by the SA node. This results in a pause in the electrical activity seen on the tracing. Remember, no electrical activity = no depolarization and contraction. Hence, a drop in blood pressure.
- The longer the pause, the further the blood pressure will drop.
- A pause of six-seconds is considered a medical emergency and emergency procedures must be initiated.
- The ECG sinus arrest rhythm typically will demonstrate constant R to R intervals prior to and following the pause. This pause results in the rhythm tracing presenting as irregular.
Analysis
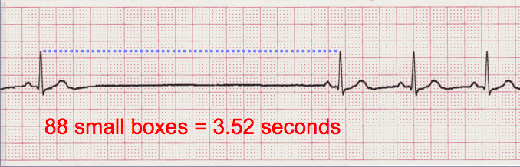
- It is important to measure the duration of the pause and report this information along with the frequency of the pauses if there are more than one.
- The pause is measured by placing your caliper tips on the last R wave just prior to the pause and the R wave immediately following the pause. Count the number of small boxes and multiply by 0.04 second. This will be reported as part of the interpretation.
Practice Strip
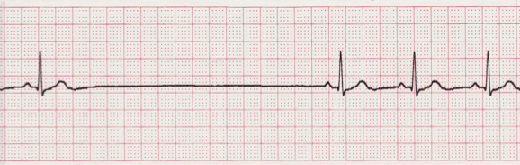
Analyze this tracing using the five steps of rhythm analysis.
Show Answer
- Rhythm: Irregular
- Rate: 40 bpm
- P wave: upright and uniform
- PR interval: 0.16 sec
- QRS: 0.10 sec
- Interpretation: Sinus Arrest, 3.52 second pause
Authors and Sources
Authors and Reviewers
- EKG heart rhythm modules: Thomas O'Brien.
- EKG monitor simulation developer: Steve Collmann
-
12 Lead Course: Dr. Michael Mazzini, MD.
- Spanish language EKG: Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH
- Medical review: Dr. Jonathan Keroes, MD
- Medical review: Dr. Pedro Azevedo, MD, Cardiology
- Last Update: 11/8/2021
Sources
-
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals, 5th Edition
Kathryn Booth and Thomas O'Brien
ISBN10: 1260064778, ISBN13: 9781260064773
McGraw Hill, 2019 -
Rapid Interpretation of EKG's, Sixth Edition
Dale Dublin
Cover Publishing Company -
12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac Drugs
Aaron Reed
Create Space Independent Publishing -
Heart Sounds and Murmurs: A Practical Guide with Audio CD-ROM 3rd Edition
Elsevier-Health Sciences Division
Barbara A. Erickson, PhD, RN, CCRN -
The Virtual Cardiac Patient: A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds, Murmurs, EKG
Jonathan Keroes, David Lieberman
Publisher: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin)
ISBN-10: 0781784425; ISBN-13: 978-0781784429 - Project Semilla, UCLA Emergency Medicine, EKG Training Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH