Supraventricular Tachycardia - Junctional Rhythms
Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) occurs when the heart rhythm occurs as a result of electrical impulses initiated above the ventricles at a rate of 150 - 250 bpm or more.
- What will remain will be a normal appearing and measuring QRS complex depolarizing at a rapid rate.
- As a result of the rapid rate, the SVT ECG complexes will be very close to one another.
- The T waves of the previous SVT rhythm complex will cover the P wave of the next complex. P waves will be entirely buried making it impossible to describe their morphology and measure the PR interval.
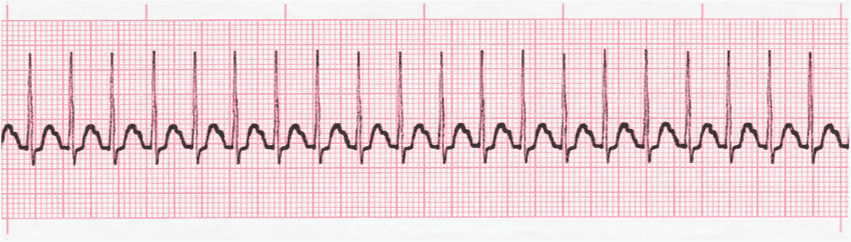
SVT Practice Strip
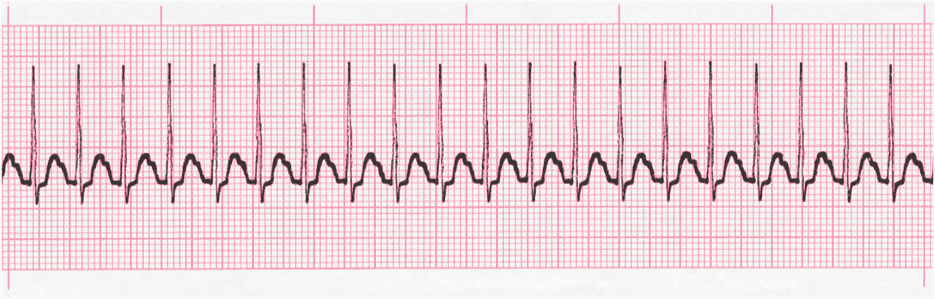
Analyze this tracing using the five steps of rhythm analysis.
Show Answer
- Rhythm: Regular
- Rate: 200
- P wave: Buried
- PR interval: Unable to measure
- QRS: 0.06 sec
- Interpretation: Supraventricular Tachycardia
Authors and Sources
Authors and Reviewers
- EKG heart rhythm modules: Thomas O'Brien.
- EKG monitor simulation developer: Steve Collmann
-
12 Lead Course: Dr. Michael Mazzini, MD.
- Spanish language EKG: Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH
- Medical review: Dr. Jonathan Keroes, MD
- Medical review: Dr. Pedro Azevedo, MD, Cardiology
- Last Update: 11/8/2021
Sources
-
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals, 5th Edition
Kathryn Booth and Thomas O'Brien
ISBN10: 1260064778, ISBN13: 9781260064773
McGraw Hill, 2019 -
Rapid Interpretation of EKG's, Sixth Edition
Dale Dublin
Cover Publishing Company -
12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac Drugs
Aaron Reed
Create Space Independent Publishing -
Heart Sounds and Murmurs: A Practical Guide with Audio CD-ROM 3rd Edition
Elsevier-Health Sciences Division
Barbara A. Erickson, PhD, RN, CCRN -
The Virtual Cardiac Patient: A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds, Murmurs, EKG
Jonathan Keroes, David Lieberman
Publisher: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin)
ISBN-10: 0781784425; ISBN-13: 978-0781784429 - Project Semilla, UCLA Emergency Medicine, EKG Training Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH