Atrial Flutter - Atrial Rhythms
Description
- Atrial Flutter (sometimes called a flutter) occurs when there is an obstruction within the atrial electrical conduction system.
- Due to this impediment a series of rapid depolarizations occur.
- These depolarizations may occur two, three, four or more times per QRS complex.
- The AV node functions like a “gatekeeper” blocking the extra impulses until the ventricular conduction system is able to accept the impulse.
- The impulse that is accepted will cause the QRS complex to occur.
Analysis
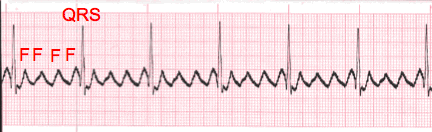
- Each atrial flutter ECG wave represents atrial depolarization. This will be noted next to the P wave step in rhythm analysis. Instead of P waves, this tracing has “F” waves. No P waves mean there is no PR interval measurement.
- When the tracing is interpreted, the ratio of F waves to each QRS complex will be documented along with the rhythm i.e. Atrial Flutter 4:1 (indicates 4 “F” waves to each QRS complex). Not all Atrial Flutter rhythm strips will have a regular rhythm. In that case just document and report your observations.
Practice Strip
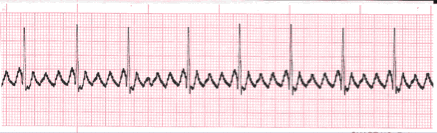
- Analyze this tracing using the five steps of rhythm analysis.
- Compare your answers with the answers on the next slide.
Practice Strip Answers

- Rhythm: Regular
- Rate: Ventricles - 80, Atria - 320
- P wave: "F" waves
- PR interval: absent
- QRS: 0.08
- Interpretation: Atrial Flutter 4:1
Authors and Sources
Authors and Reviewers
- EKG heart rhythm modules: Thomas O'Brien.
- EKG monitor simulation developer: Steve Collmann
-
12 Lead Course: Dr. Michael Mazzini, MD.
- Spanish language EKG: Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH
- Medical review: Dr. Jonathan Keroes, MD
- Medical review: Dr. Pedro Azevedo, MD, Cardiology
- Last Update: 11/8/2021
Sources
-
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals, 5th Edition
Kathryn Booth and Thomas O'Brien
ISBN10: 1260064778, ISBN13: 9781260064773
McGraw Hill, 2019 -
Rapid Interpretation of EKG's, Sixth Edition
Dale Dublin
Cover Publishing Company -
12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac Drugs
Aaron Reed
Create Space Independent Publishing -
Heart Sounds and Murmurs: A Practical Guide with Audio CD-ROM 3rd Edition
Elsevier-Health Sciences Division
Barbara A. Erickson, PhD, RN, CCRN -
The Virtual Cardiac Patient: A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds, Murmurs, EKG
Jonathan Keroes, David Lieberman
Publisher: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin)
ISBN-10: 0781784425; ISBN-13: 978-0781784429 - Project Semilla, UCLA Emergency Medicine, EKG Training Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH