Step 3 P wave Morphology (Shape) - Cardiac Rhythms
Description
- The lead most commonly referenced in cardiac monitoring is lead II.
- For the purposes of this training module, lead two will specifically be referenced unless otherwise specified.
- The P wave in lead II in a normal heart is typically rounded and upright in appearance.
- Changes in shape must be reported. This can be an indicator that the locus of stimulation is changing or the pathway taken is changing.
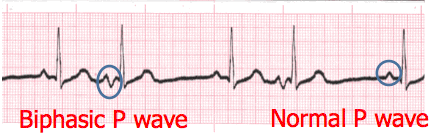
- P waves may come in a variety of morphologies i.e. rounded and upright, peaked, flattened, notched, biphasic (second complex, pictured), inverted and even buried or absent!
- Remember to describe the shape. This can be very important to the physician when diagnosing the patient.
P Wave Practice 1
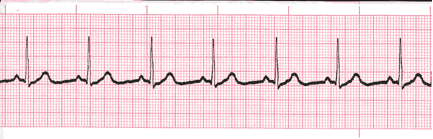
Analyze this tracing. Describe the P waves.
Reveal Answer
Upright and uniformP Wave Practice 2
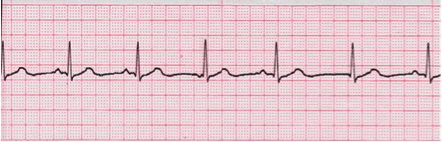
Analyze this tracing. Describe the P waves.
Reveal Answer
Variable, upright, inverted and absentAuthors and Sources
Authors and Reviewers
- EKG heart rhythm modules: Thomas O'Brien.
- EKG monitor simulation developer: Steve Collmann
-
12 Lead Course: Dr. Michael Mazzini, MD.
- Spanish language EKG: Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH
- Medical review: Dr. Jonathan Keroes, MD
- Medical review: Dr. Pedro Azevedo, MD, Cardiology
- Last Update: 11/8/2021
Sources
-
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals, 5th Edition
Kathryn Booth and Thomas O'Brien
ISBN10: 1260064778, ISBN13: 9781260064773
McGraw Hill, 2019 -
Rapid Interpretation of EKG's, Sixth Edition
Dale Dublin
Cover Publishing Company -
12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac Drugs
Aaron Reed
Create Space Independent Publishing -
Heart Sounds and Murmurs: A Practical Guide with Audio CD-ROM 3rd Edition
Elsevier-Health Sciences Division
Barbara A. Erickson, PhD, RN, CCRN -
The Virtual Cardiac Patient: A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds, Murmurs, EKG
Jonathan Keroes, David Lieberman
Publisher: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin)
ISBN-10: 0781784425; ISBN-13: 978-0781784429 - Project Semilla, UCLA Emergency Medicine, EKG Training Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH