EKG Training, Practice and Quiz
We provide a wide range of EKG rhythm strip training with an emphasis on practice, coaching and quizzes. Use this page to access these training materials and web apps:
EKG Practice Drills and Tests
The EKG practice tests (drills) provide a fast and interactive method for EKG strip practice. Users are asked to interpret the EKG using a multiple choice format. Immediate feedback is available after answering each question. These EKG practice tests can be used on desktops, tablets and smartphones.
EKG Practice DrillsEKG Quizzes
Our EKG rhythm practice strip present 25 tracings for EKG interpretation. These graded EKG quizzes can be selected based upon the user's educational objectives. Quiz EKG tracings are randomly selected from our database of over 600 tracings, so the quiz can be repeated many times. Scoring as well as immediate answer feedback are provided. Our quizzes include:
- Comprehensive (over 50 categories)
- Physician Assistant
- Nurse Practitioner
- EKGs for Nurses
- EKGs for ACLS
- EKGs for NCLEX Prep
- Patient Monitor Simulator
- Basic EKG Quizzes - Standardized
EKG Training Modules
We are pleased to announce our new EKG training modules. These modules provide in-depth training in EKG basics, rhythm analysis and a wide range of EKG topics. Each module includes lessons, interactive drills and a course quiz.
EKG Training ModulesEKG Interpretation Practice Coach
Our EKG coach breaks down interpretation into five analysis steps followed by classification of the EKG tracing. Scoring based upon both analysis and interpretation are available..
EKG Rhythm Interpretation CoachEKG Monitor Quiz
Our new, advanced, patient monitor simulator, developed by Steve Collmann:Advanced EKG Monitor Quiz
EKG Interpretation Cheat Sheets
Our EKG Interpretation Cheat Sheets provides information on reading EKG strips with over forty different abnormal EKG examples. For each arrhythmia, there are EKG strip examples and descriptive text with qualifying criteria. We also provide an annotated tracing with a summary of the key features and values.
EKG Reference Guide12 Lead EKG
Practice 12 lead EKG interpretation coaching with step-by-step feedback.
12-Lead EKG Interpretation CoachingA slide presentation on 12 lead EKG interpretation.
12-Lead EKG LectureSpanish Edition
In cooperation with Project Semilla, we have created Spanish Editions of several of our EKG training modules. These are hosted by our sister website: PracticalClinicalSkills.com.
Ejercicios de práctica de ritmos cardíacosGuía de referencia de los ritmos cardíacos
Paciente Virtual Prueba con Monitor
French, German & Spanish EKG Courses
EKG-SchulungEntrenamiento-EKG
Entrainement-ECG
EKG Definition
An EKG, also called an ECG or electrocardiogram, is a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is a quick and painless procedure. EKGs captures a tracing of cardiac electrical impulse as it moves from the atrium to the ventricles. These electrical impulses cause the heart to contract and pump blood. EKGs are interpreted by medical professionals to understand the following:
- Heart rate
- Heartbeat regularity
- Strength and timing of the electrical signals
- Any possible abnormal conditions
Abnormal EKG Strips
A summary of each of the most common EKG types is provided below.
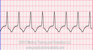
The EKG rhythm will appear regular. The heart rate is 50-120 bpm, which is faster than a ventricular rhythm but slower than ventricular tachycardia. The P wave is absent and PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be wide (>0.10 sec) and bizarre looking.
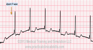
The EKG rhythm will appear regular with heart rate that is normal (60-100 bpm). The P wave is present before, during (hidden) or after QRS. If visible it is inverted. The PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec).

Cardiac electrical activity is absent. No EKG rhythm can be observed. The P wave and QRS complex are not visible. Confirm using multiple leads.
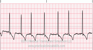
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular. Heart rate is very fast: over 350 bpm for atrial, but ventricular rate may be slow, normal or fast. The P wave features are absent - erratic waves are present. The PR interval is absent. The QRS complex will typically be normal but may be widened if there are conduction delays.
Please enroll in one of our paid plans to view an additional 35 EKG abnormalities. Use the Join button in the upper right of this page.
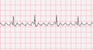
The atrial heart rate is rapid (250-350 bpm), but ventricular rate is often slower. EKG rhythm will appear regular. P wave and PR interval are not observable, but saw-toothed flutter waves are present. The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec).
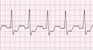
The EKG rhythm P wave features should appear normal and the PR interval is normal (0.12-0.20 sec). The QRS complex will typically be wide (>0.12 sec).
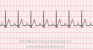
The P wave will be normal while the PR interval is prolonged (>0.20 sec). The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec). A first degree av block occurs when electrical impulses moving through the atrioventricular (AV) node are delayed (but not blocked). The adjective first degree indicates slowed conduction without missed beats.
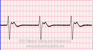
The EKG rhythm will appear regular with a very slow heart rate(20-40 bpm). The P wave will be absent and the PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be wide (>0.10 sec) and a bizarre appearance.
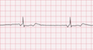
The EKG rhythm will appear regular. Heart rate that is slow (40-60 bpm). The P wave will be present before, during (hidden) or after QRS, if visible it is inverted. The PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec).
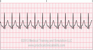
The EKG rhythm will appear regular with a fast heart rate (100-180 bpm). The P wave can appear before, during (hidden) or after QRS, if visible it is inverted. Observe that the PR interval is absent or short. The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec).

The EKG rhythm will appear irregular with a fast heart rate (> 100 bpm). The P wave features often change shape and size from beat to beat with at least three differing forms. Observe that the PR interval is variable. The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec). In addition, the T wave can be distorted.
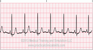
The EKG rhythm will appear regular with a normal (60-100 bpm) heart rate. The P wave appears normal and precedes each QRS. Observe that the PR interval is normal (0.12-0.20 sec). The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec).
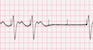
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular with heart rate that is slow or normal. Observe that the pacemaker spikes are not followed by p waves or QRS complexes.
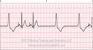
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular and pacemaker spikes do not appear.
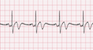
The EKG rhythm will appear regular with heart rate that is normal. The P wave and PR interval will both appear normal. The QRS complex is also normal. Pacemaker spikes will precede the P wave.
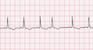
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular with heart rate that is usually normal but depends on underlying rhythm. The P wave will appear premature, positive and a shape that is abnormal. Observe that the PR interval is normal or longer. The QRS complex will typically be 0.10 sec or less.
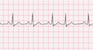
The EKG rhythm will appear regular with premature beats with heart rate that is the underlying rate. The P wave is present before, during (hidden) or after QRS. If the P wave is visible, it is inverted. Observe that the PR interval is absent or short. The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec).
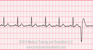
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular with heart rate that is the underlying rate. The P wave features absent. Observe that the PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be wide (> 0.10 sec) with a bizarre appearance.
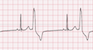
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular with an absent P wave and the PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be wide (> 0.10 sec) with a bizarre appearance. The PVC appears on every second beat.
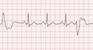
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular. The P wave is absent and the PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be wide (> 0.10 sec) and bizarre in appearance. The PVC appears every fourth beat.

The EKG rhythm will appear irregular. The P wave is absent and the PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be wide (> 0.10 sec) with a bizarre appearance. The PVC appears every third beat.
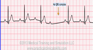
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular but with progressively longer pr interval lengthening. The P wave is normal. Observe that the PR interval becomes progressively longer until a QRS complex is missed, then cycle repeats. The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec).
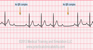
The EKG rhythm will appear regular (atrial) and irregular (ventricular) with heart rate that is characterized by atrial rate that is usually faster than ventricular rate (usually slow). The P wave has a normal form, but more P waves than QRS complexes. The PR interval is normal or prolonged. The QRS complex will typically be normal or wide.
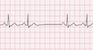
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular when SA block occurs with a normal or slow heart rate. The P wave will be normal and the PR interval will be normal (0.12-0.20 sec). The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec). The pause time is an integer multiple of the p-p interval.
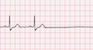
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular due to a pause. Heart rate will be normal to slow. The P wave is normal. The PR interval is normal (0.12-0.20 sec). The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec). Pause time is not an integer multiple of the p-p interval.
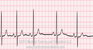
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular, varying with respiration with heart rate that is normal (60-100 bpm) and rate may increase during inspiration. The P wave is normal and the PR interval is also normal (0.12-0.20 sec). The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec). Heart rate frequently increases with inspiration, decreasing with expiration.
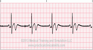
The EKG rhythm will appear regular with a slow heart rate (under 60 bpm). The P wave and the PR interval are normal. The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec).
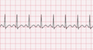
The EKG rhythm will appear regular with a fast heart rate (> 100 bpm). The P wave will be normal but may merge with T wave at very fast rates. Observe that the PR interval is>normal (0.12-0.20 sec). The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec). The QT interval shortens with increasing heart rate.
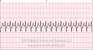
The EKG rhythm will appear regular and heart rate that will be fast (150-250 bpm). The P wave will be merged with T wave. The PR interval is normal (0.12 sec) but can be difficult to measure. The QRS complex will typically be normal (.10 sec).
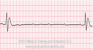
The EKG rhythm will appear regular, but atrial and ventricular rhythms are independent. Heart rate is characterized by atrial rate usually normal but faster than the ventricular rate. The P wave will have normal shape and size but may appear within QRS complexes. The PR interval is absent: the atria and ventricles beat independently. The QRS complex will typically be normal, but wide if junctional escape focus.

The EKG rhythm will appear highly irregular with an unmeasurable heart rate. The P wave is absent, the PR interval is not measurable and no QRS complex. The EKG tracings is a wavy line.
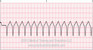
The EKG rhythm will appear regular with heart rate that is fast (100-250 bpm). The P wave is absent and the PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be wide (>0.10 sec) with a bizarre appearance.
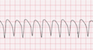
The EKG rhythm will appear regular with a fast (100-250 bpm) heart rate. The P wave is absent and the PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be wide (>0.10 sec) and bizarre looking.
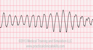
The EKG rhythm will appear regular or irregular with heart rate that is fast (100-300 bpm). The P wave is absent and the PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be normal or wide (>0.10 sec) with a bizarre shape.
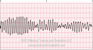
The EKG rhythm will appear irregular with heart rate that is fast (200-250 bpm). The P wave is absent and the PR interval is not measurable. The QRS complex will typically be wide (>0.10 sec). Its shape is characterized by a gradual change in the EKG amplitude and a twisting of the QRS complexes around a line.
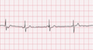
The EKG rhythm will appear to be irregular with a normal heart rate. The P wave can be observed changing shape and size from beat to beat (at least three different forms). The PR interval is variable in duration. The QRS complex will typically be normal (0.06-0.10 sec) and the T wave normal. If heart rate exceeds 100 bpm, then rhythm may be multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT).
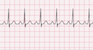
The EKG rhythm will appear regular unless atrial fibrillation present. Heart rate is normal (60-100 bpm). The P wave is normal. Observe that the PR interval is can be short (less than 0.12 sec). The QRS complex will typically be wide (over 0.12 sec). A delta wave (positive or negative) distorts the early part of the QRS complex.
Authors and Reviewers
- EKG heart rhythm modules: Thomas O'Brien.
- EKG monitor simulation developer: Steve Collmann
-
12 Lead Course: Dr. Michael Mazzini, MD.
- Spanish language EKG: Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH
- Medical review: Dr. Jonathan Keroes, MD
- Medical review: Dr. Pedro Azevedo, MD, Cardiology
- Last Update: 11/8/2021
Sources
-
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals, 5th Edition
Kathryn Booth and Thomas O'Brien
ISBN10: 1260064778, ISBN13: 9781260064773
McGraw Hill, 2019 -
Rapid Interpretation of EKG's, Sixth Edition
Dale Dublin
Cover Publishing Company -
12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac Drugs
Aaron Reed
Create Space Independent Publishing -
Heart Sounds and Murmurs: A Practical Guide with Audio CD-ROM 3rd Edition
Elsevier-Health Sciences Division
Barbara A. Erickson, PhD, RN, CCRN -
The Virtual Cardiac Patient: A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds, Murmurs, EKG
Jonathan Keroes, David Lieberman
Publisher: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin)
ISBN-10: 0781784425; ISBN-13: 978-0781784429 - Project Semilla, UCLA Emergency Medicine, EKG Training Breena R. Taira, MD, MPH