What is a Sinus Rhythm?
This page provides an introduction to sinus rhythms and links to our EKG interpretation courses and drills.
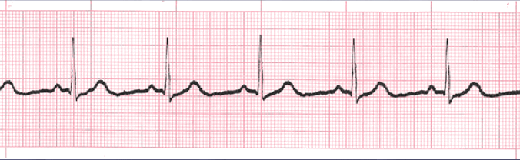
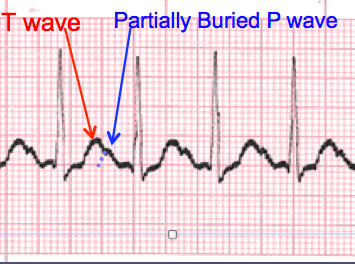
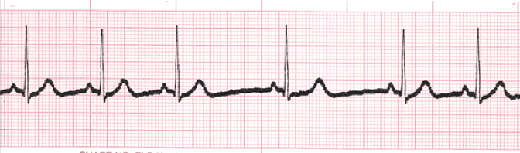
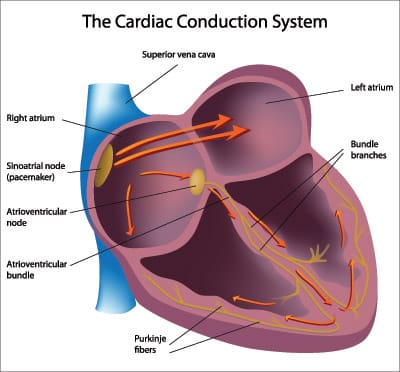
A normal sinus rhythm refers to both a normal heart rate and rhythm. Normal heart rates are from 60 to 100 beats per minute. The shape of the electrocardiogram (EKG) tracing will exhibit certain key attributes to be considered normal, as discussed below. With normal sinus rhythms, the heart beat's electrical impulse originates in the sinoatrial node (SA). The P waves are upright and appear before each QRS and have the same shape. The intervals between the P waves are regular, although some variations can occur with respiration. Sinus rhythms are classified as:
- Normal Sinus Rhythm
- Sinoatrial Block
- Sinus Pause
- Sinus Arrhythmia
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Sinus Tachycardia
Sinus Rhythm Categories
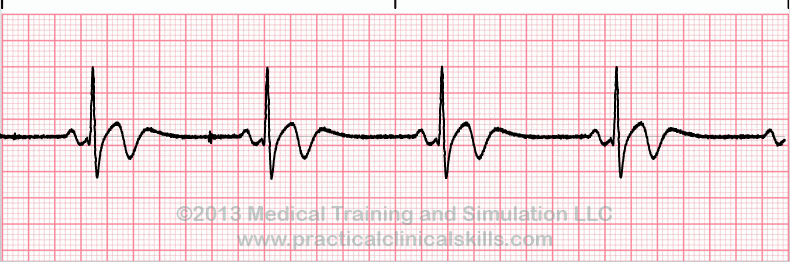
Normal Sinus Rhythm
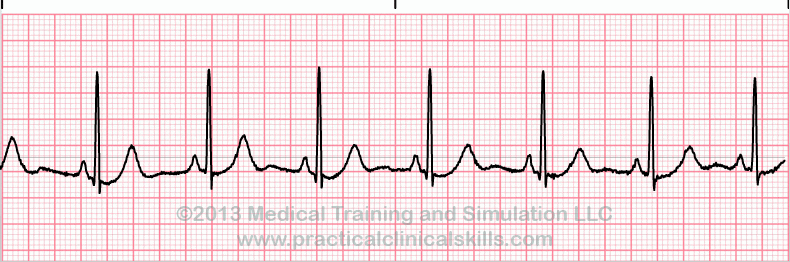
This is the normal sinus rhythm of the heart. The electrical impulse originates within the SA node and travels through the atria to the AV node. After a brief delay, the impulse travels down the bundle branches, thought the Purkinje fibers to the ventricles.
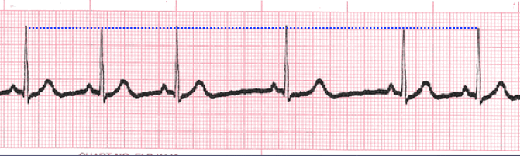
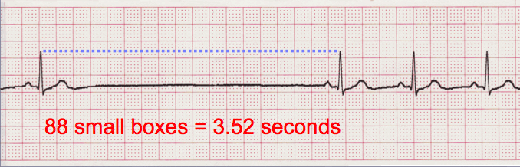
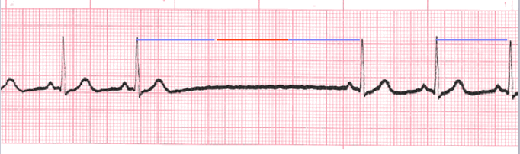
Sinus Pause
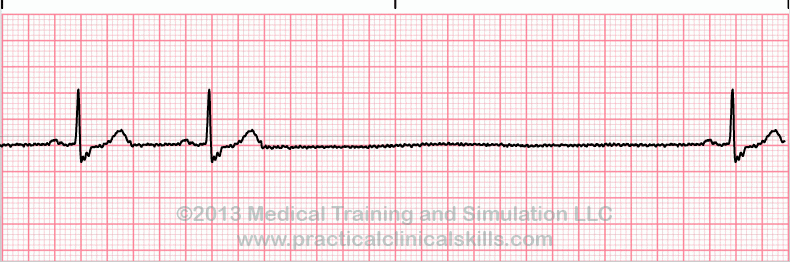
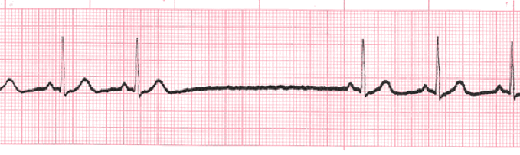
Sinus pause includes sinus arrest and sinus exit block. Sinus arrest is caused by failure of the SA node to create an impulse. An interruption in R-R regularity can be observed. With sinus exit block the SA node generates an impulse but it is blocked before being transmitted through the atria. R-R regularity continues with the beats that follow the missed beat. Depressed ST segments can also be observed.
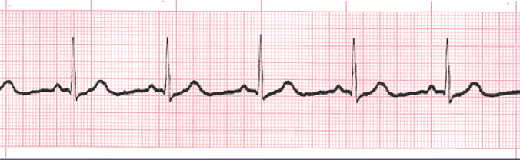
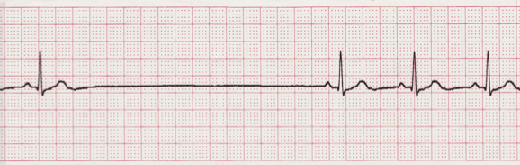
Sinus Arrhythmia
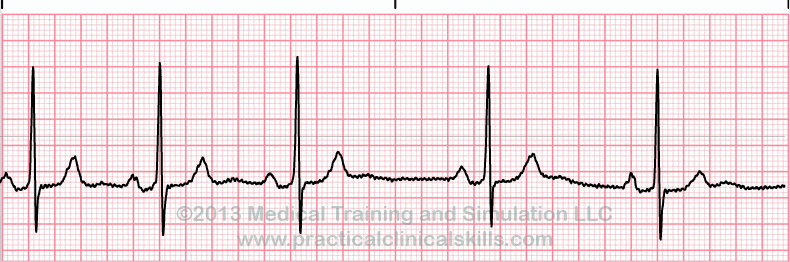
Sinus arrhythmia looks normal except for slight irregularities. A frequent cause of sinus arrhythmia can be rhythm variations caused by respiration.
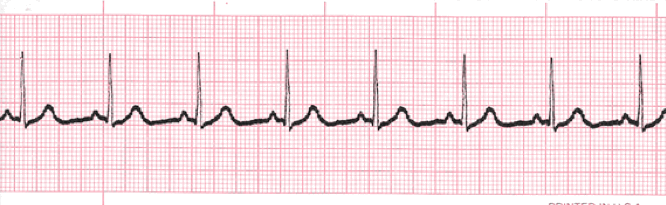
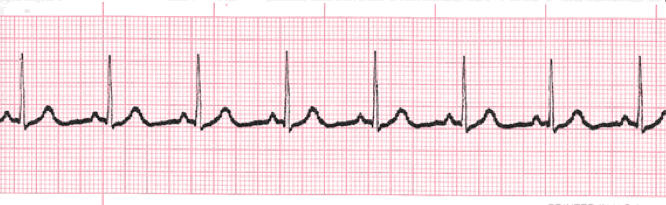
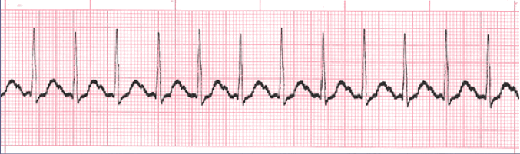
Sinus Tachycardia
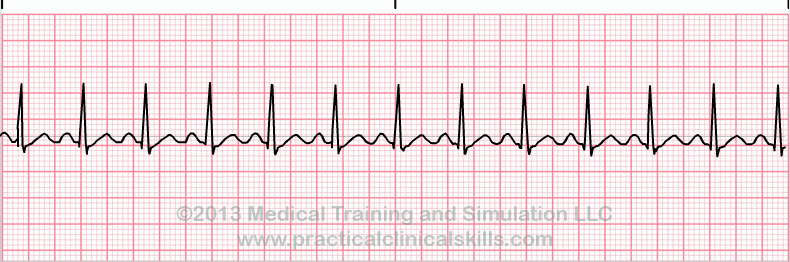
Sinus tachycardia is a normal sinus rhythm, but with a heart rate over 100 bpm. It is a normal response to exercise, excitement and some illnesses.